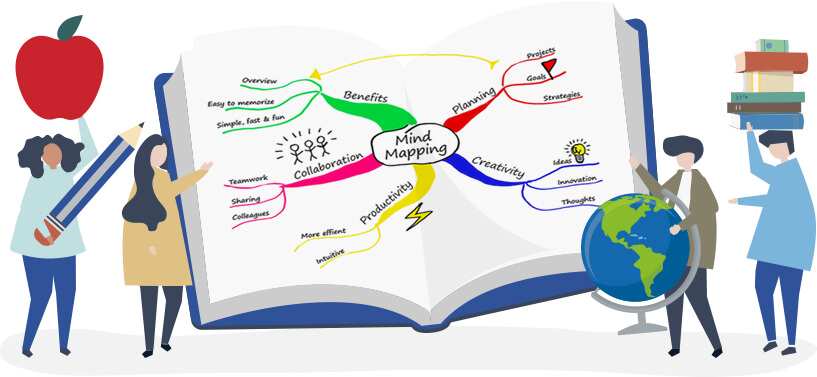
A recent Johns Hopkins study shows that when students utilize Mind Mapping, grades increase by 12%.
This increase is attributed to how Mind Mapping helps students to organize ideas and understand concepts better. Not only does this speed up the time it takes to learn new information but it embeds this new information into the long-term memory more effectively. Adding colors and images on Mind Maps can help students further by using visual cues to recall information at a later stage, such as during exams or presentations.
Although educators and students have been drawing concept maps and mind maps on paper for many years, this has changed with the introduction of visual thinking software, in particular Mind Mapping. These tools have automated the Mind Mapping process, making it more efficient to brainstorm concepts as ideas or branches. Furthermore, some Mind Mapping software integrates with MS Office and Google, allowing students to convert their ideas into other documents such as Word or PowerPoint.
Let's dive into this a little bit further. A typical essay or assignment is often written in a linear or hierarchical format (top down). However, that format can be difficult to work with, especially for students who struggle to sequence information in this way.
Mind Mapping is a non-linear or radial way to organize information and is more suited to the organic method of thinking. Mind Maps make generating ideas easier and help articulate thoughts more coherently.
Mind Mapping is widely promoted by educationalists as an assistive tool for students with Special Learning Differences such as Dyslexia and Autism Spectrum Condition (ASC).
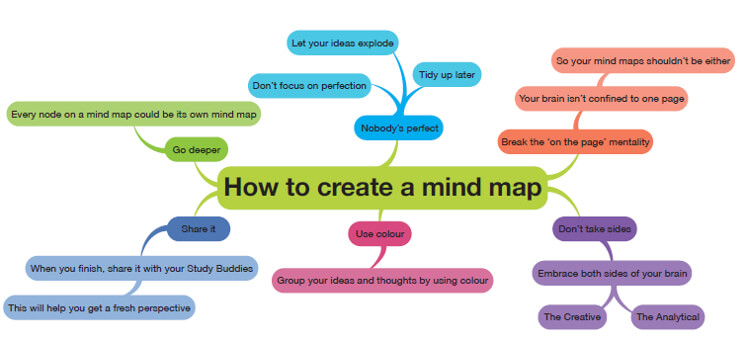
Credit - University of Huddersfield: A Quick Start Guide
A Learning Difference or Neurodiversity is defined as "a condition giving rise to difficulties in acquiring knowledge and skills to the level expected of those of the same age, especially when not associated with a physical handicap".
While there are many different learning differences or neurodiversities, a lot of the diagnoses share the same symptoms. For example, Dyslexia, ASD, ADHD and APD share at least one of the symptoms of poor memory retention, trouble processing and organizing information or communication difficulties. (Read More About Mind Mapping as an AT tool)
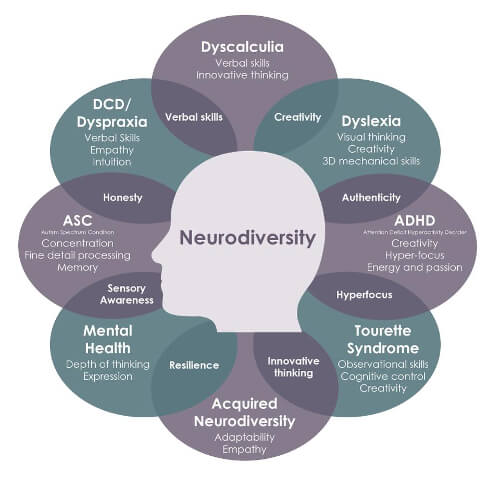
Credit: Dr Nancy Doyle, Genius Within CIC, based on the work of Mary Colley
While there are many different learning differences or neurodiversities, a lot of the diagnoses share the same symptoms. For example, Dyslexia, ASD, ADHD and APD share at least one of the symptoms of poor memory retention, trouble processing and organizing information or communication difficulties. (Read More About Mind Mapping as an AT tool)
The British Dyslexia Association states, "Dyslexics struggle with their spoken and/or written language, following instructions, poor concentration and carrying out analytical or logical tasks. Strategies such as mind mapping are recognized as valuable learning tools." Reference: The British Dyslexia Association, www.bdadyslexia.org.uk.
Sounds familiar? Those are common struggles of Dyslexic learners. Although many learners embrace Mind Mapping using pen and paper, there are several software programs that can make the Mind Mapping process less cumbersome and more engaging. (Read More About Mind Mapping as an AT tool)

Although ASD is considered the mildest form of Autism, there are many common struggles students and working professionals must overcome to function effectively in their daily activities. Sometimes referred to as 'high functioning autism', ASD impacts communication, organization and memory.
To find out more about how Mind Mapping helps individuals with ASD (Read More About Mind Mapping as an AT tool).